Polyamine Biosynthesis in Plants
Polyamines are certain biogenic di-, tri-, and tetra-amines which are derived from amino acids. In general, the compounds putrescine,
spermine, and spermidine, sometimes also cadaverine are summarized as polyamines. The names of these substances are derived from their isolation
from putrefying meat (putrescine), dead human bodies (cadaverine) (Brieger, 1885) and semen (Ladenburg and Abel, 1888; Dudley et al., 1927).
Today it is clear that polyamines are present in all living organisms and that they have essential functions for cell growth and propagation. For
the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana it has recently been shown that defects in the biosynthesis of putrescine and spermidine results in an
embryo-lethal phenotype (Imai et al., 2004;
Urano et al., 2005).
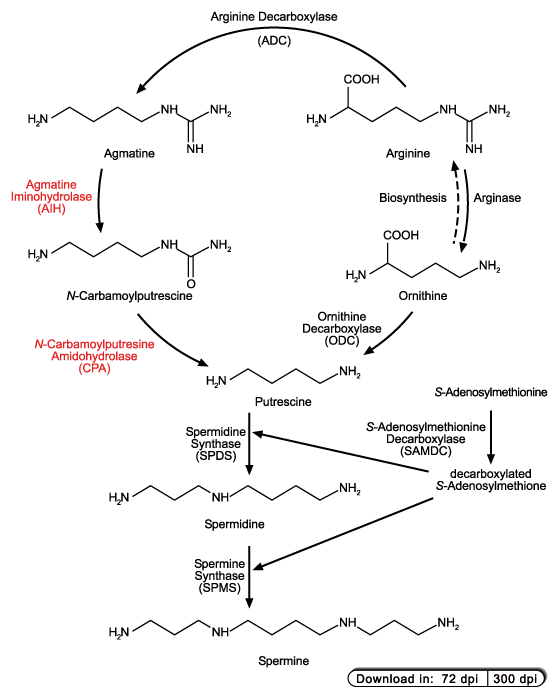
Spermine and Spermidine are produced from putrescine by the subsequent addition of aminopropyl groups derived from S-adenosylmethionine. Putrescine
is derived from either arginine or ornithine by two different pathways, the arginine decarboxylase pathway (ADC pathway) or the ornithine decarboxylase
pathway (ODC pathway), respectively. In plants both pathways occur, however, Arabidopsis thaliana has lost the ODC gene (Hanfrey et al., 2001)
but instead has two ADC genes (Watson et al., 1997).
In the course of our research on plant nitrilases we identified three cDNA sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana which encode for enzymes similar
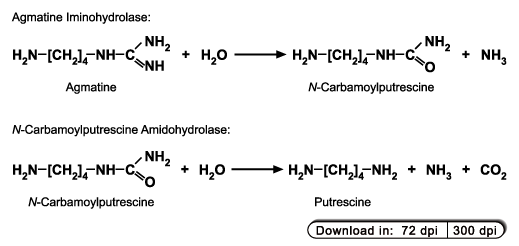
to nitrilases. One of these, the "nitrilase-like protein 1" (NLP1) was subsequently identified as N-carbamoylputrescine amidohydrolase (CPA), the
enzyme of the ADC pathway which catalyses the formation of putrescine from N-carbamoylputrescine (Piotrowski et al., 2003).
Shortly afterwards we identified the cDNA for agmatine aminohydrolase (AIH) of Arabidopsis thaliana (Janowitz et al., 2003).
Although AIH also catalyzes the hydrolysis of a C-N bond it does not belong to the C-N-hydrolase family. Instead AIH is related to other enzymes which act on guanidino
groups (guanidino-group modifying superfamily, GMSF) (Shiray et al., 2001).
Interestingly, certain giant viruses of the Phycodnaviridae (DNA viruses which infect algae) also contain polyamine biosynthesis genes, including genes for AIH and CPA.
We could recently show that each of the two genes from three different chloroviruses encode functional AIH and CPA enzymes, respectively (Baumann et al., 2007).
Unlinked References
- Brieger, L. (1885) Ueber Ptomaine. Aug. Hirschwald, Berlin
- Ladenburg, A. and Abel, J. (1888) Ueber das Aethylenimin (Spermin?). Ber. Deutsch. Chem. Ges. 21:758-766
- Watson, M.B., Yu, W., Galloway, G.L., and Malmberg, R.L. (1997) Isolation and characterization of a second arginine decarboxylase cDNA from Arabidopsis (AF009647)(PGR97-114). Plant Physiol. 114:1560